Python Prompt Toolkit 2.0¶
Warning
Notice that this is the prompt_toolkit 2.0 documentation. It is incompatible with the 1.0 branch, but much better in many regards. Please read Upgrading to prompt_toolkit 2.0 for more information.
prompt_toolkit is a library for building powerful interactive command line and terminal applications in Python.
It can be a very advanced pure Python replacement for GNU readline, but it can also be used for building full screen applications.
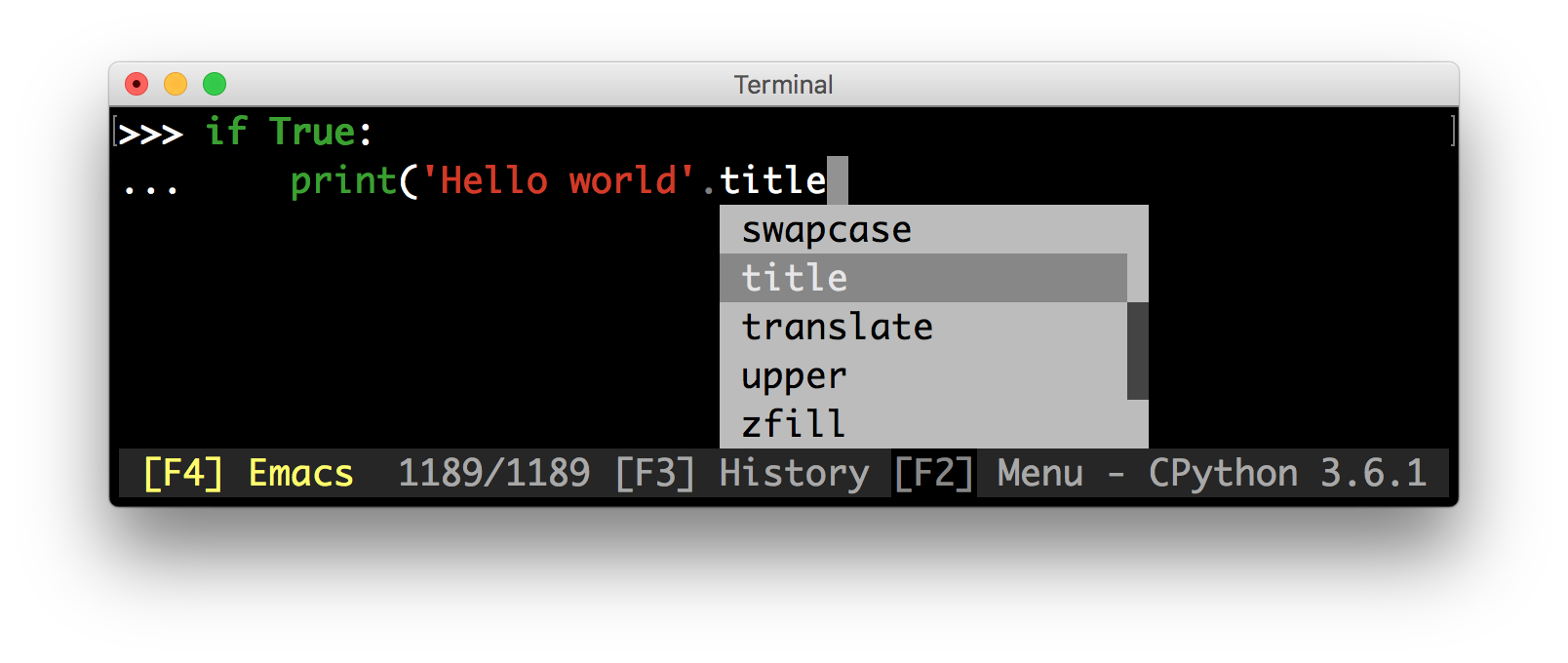
Some features:
- Syntax highlighting of the input while typing. (For instance, with a Pygments lexer.)
- Multi-line input editing.
- Advanced code completion.
- Selecting text for copy/paste. (Both Emacs and Vi style.)
- Mouse support for cursor positioning and scrolling.
- Auto suggestions. (Like fish shell.)
- No global state.
Like readline:
- Both Emacs and Vi key bindings.
- Reverse and forward incremental search.
- Works well with Unicode double width characters. (Chinese input.)
Works everywhere:
- Pure Python. Runs on all Python versions from 2.6 up to 3.4.
- Runs on Linux, OS X, OpenBSD and Windows systems.
- Lightweight, the only dependencies are Pygments, six and wcwidth.
- No assumptions about I/O are made. Every prompt_toolkit application should also run in a telnet/ssh server or an asyncio process.
Have a look at the gallery to get an idea of what is possible.
Getting started¶
Go to getting started and build your first prompt.
Thanks to:¶
A special thanks to all the contributors for making prompt_toolkit possible.
Also, a special thanks to the Pygments and wcwidth libraries.